About Obamacares Optional 35% Fee For Selling Insurance
ObamaCare gives states and the federal government the option of charging insurance companies a 3.5% fee on the cost of the premium to sell insurance on the exchange. States have the option of using grants and other forms of assistance from the federal government however, states that refuse to set up a state-run exchange will not get the subsides , therefore their constituents may see the results of this tax passed along to them in the form of higher premiums.
Despite the cost, insurance companies have a big incentive to sell their plans on the exchange since it gives them access to millions of Americans who will only be able to apply their tax credits and subsidies on the exchanges.
How the 3.5% fee will affect States of who are opting out of setting up an exchange and how it will affect the price of insurance premiums remains to be seen. There are a lot of factors that go into which plans are offered in which regions and by which insurers, so pinpointing the results of the 3.5% fee isnt easy. On our site, we will attempt to cover the results of each states choices moving forward in more detail.
Three Key Challenges Faced By Ffes
Making the new Exchange market work under any set of factors is challenging, as this new subsidized insurance market is complex to operate and must mesh with other critical state policies, in particular, state insurance regulation and Medicaid operations. Furthermore, millions of consumers will need help understanding the new market and learning how to use its benefits. But special considerations arise in the case of FFEs, because the ACA envisions such a strongly state-based approach to health reform implementation. Three of the biggest challenges are discussed hereafter.
Background: Types Of Marketplaces
Under the ACA, each state must either operate its own marketplace or rely on the federal marketplace to handle exchange functions such as certifying health plans that meet ACA standards and determining eligibility for exchange plans and subsidies.
In most states, the federal government runs the marketplace. The federal platform called HealthCare.gov handles eligibility and enrollment functions and the call center for consumers, and the marketplace collects a user fee from the insurers offering plans through it. The fee is 3.0 percent of exchange plan premiums in 2020.
Thirteen states run their own SBMs, meaning they take charge of all required functions and have their own systems for conducting eligibility and enrollment, operating a call center, and conducting consumer outreach and plan certification. These states pay no user fees to the federal government.
Another six states have a hybrid between the two: SBMs on the federal platform, or SBM-FPs, which take charge of many marketplace functions but rely on the federal HealthCare.gov platform to conduct eligibility and enrollment and operate a call center. These states pay the federal government a user fee that is set at a lower rate compared to full FFMs.
The rest of this paper presents seven recommendations for states that have decided to move forward with SBM transitions.
Read Also: How Much Does Starbucks Health Insurance Cost
What Is The Obamacare Subsidy
The Obamacare subsidy is really a tax credit, and it is formally known as the Advanced Premium Tax Credit . Typically people receive a tax credit at the end of the year when filing taxes, but this tax credit can be received in advance, during the year, to reduce the monthly premium costs of an Obamacare health insurance plan.
You must complete an official federal government application to learn your subsidy amount. Everyones amount will be different. The calculation for the subsidy amount can be quite complicated. It is based on several different factors, but household income is the main factor. We recommend using our tool to estimate your subsidy amount.
Understanding The Ny State Health Benefits Exchange
Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, otherwise known as the Affordable Care Act, every state is required to have its own Health Insurance Exchange for health coverage.
The New York State Health Benefits Exchangeofficially called NY State of Health – The Official Health Plan Marketplaceis a one-stop-shop website for information on and access to quality, affordable health insurance. New Yorkers in need of health coverage who meet certain rules established by the law can visit this site to:
- Compare private commercial insurance options.
- Calculate insurance costs.
- Enroll in a plan .
The Affordable Care Act also requires that all the plans and features are presented in a uniform manner and show the cost of coverage without hidden fees. This consistency is by design: uninsured and under-insured people can select insurance based on an apples-to-apples comparison of products.
Recommended Reading: Does Starbucks Provide Health Insurance For Part Time Employees
Economics Of Health Insurance Exchanges: The Individual Mandate
The health insurance advocacy group America’s Health Insurance Plans was willing to accept these constraints on pricing, capping, and enrollment because of the individual mandate: The individual mandate requires that all individuals purchase health insurance. This requirement of the ACA allows insurers to spread the financial risk of newly insured people with pre-existing conditions among a larger pool of individuals.
Additionally, a study done by Pauly and Herring estimates that individuals with pre-existing conditions in the 99th percentile of financial risk represented 3.95 times the average risk . Figures from the House Committee on Energy and Commerce would indicate that approximately 1 million high-risk individuals will pursue insurance in the health benefits exchanges. Congress has estimated that 22 million people will be newly insured in the health benefits exchanges. Thus the high-risk individuals do not number in high enough quantities to increase the net risk per person from previous practice. It is thus theoretically profitable to accept the individual mandate in exchange for the requirements presented in the ACA.
Purchasing Health Care Coverage Through The Marketplace And Reporting Changes
Each year the Health Insurance Marketplace has an open enrollment period and special enrollment periods for eligible taxpayers. For information about enrollment periods, visit HealthCare.gov or contact your state-based Marketplace.
If you enrolled in insurance coverage through the Marketplace, you should report any changes in your circumstances like changes to your household income or family size to the Marketplace when they happen. Changes in circumstances may affect your advance payments of the premium tax credit. When you report a change in circumstances, you may become eligible for a special enrollment period, which allows you to purchase health care insurance through the Marketplace outside of the open enrollment period. Visit the Marketplace at HealthCare.gov for more information about reporting changes in circumstances and special enrollment.
To estimate the effect that changes in circumstances may have upon the amount of premium tax credit that you can claim – see the Premium Tax Credit Change Estimator on our Affordable Care Act Estimator Tools page.
Find out more about the Premium Tax Credit and other tax provisions of the Affordable Care Act at IRS.gov
Read Also: Starbucks Employee Health Insurance
Commit To A No Wrong Door Eligibility And Enrollment System
An especially critical area for SBMs to focus on is providing the no wrong door eligibility process that the ACA envisions, in which people submit one application and then can easily enroll in the health program for which they are eligible: an exchange plan, Medicaid, or CHIP. The no wrong door concept applies to all health insurance marketplaces, meaning they must provide at least minimal coordination across programs. But when a state administers both the marketplace and Medicaid, it can do far better than the FFM in this area.
One way to achieve no wrong door is to integrate the SBMs eligibility process with that of other health programs, including Medicaid, as most first-generation SBMs did. This has clear advantages. Integrated eligibility systems are far better at providing a no wrong door experience than the FFM, which usually transmits information to state Medicaid agencies about applicants who appear likely eligible for Medicaid. Such transfers can be complex and require applicants to provide additional or duplicative information. An integrated system also provides a more streamlined process for enrollees, for example by allowing them to move more seamlessly from one program to another if their eligibility changes and by simplifying the eligibility and enrollment process when families have members who qualify for different programs.
A Primer To State Exchanges: State Health Insurance Marketplace Facts
A Primer to the State Exchanges: States have either implemented a state-run health insurance exchange or let the federal government run the health insurance exchange for them. Some states have taken a variation on the approach by partnering with another state or the federal government. No matter what approach your State took, the way you shop for insurance is the same. Find your states marketplace below and apply so that youre ready to get cost assistance, enroll in a plan, or change plans during open enrollment.
Insurance must be obtained during open enrollment.
The only way to qualify for and use cost assistance is through the marketplaces.
Over half of uninsured Americans will get cost assistance on their states health insurance exchange marketplace resulting in free or low-cost health insurance.
Marketplace plans are known as metal plans. The more precious the metal, the better the plan. All metal plans qualify for tax credits, but only Silver plans qualify for out-of-pocket assistance through Cost Sharing Reduction subsidies.
All marketplace plans must offer ten essential benefits with no lifetime or annual dollar limits, include free preventive services and an annual wellness visit, have at least a 60% actuarial value, and cap deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums.
You cant be charged more based on health status or gender.
Sometimes health insurance exchanges are called health insurance marketplaces.
Read Also: Does Starbucks Provide Health Insurance For Part Time Employees
How Federal Subsidies Work With State Based Plans
While many people believe that state based plans are only available for people with low incomes, the truth is that they actually benefit a large portion of the middle class. The reason for this is that federal subsidies on state-based health insurance plans apply for people within certain income brackets. If you earn between 133 percent and 400 percent of the federal poverty level, then you qualify for federally supported state-based health insurance. That means that your monthly premiums for your state based health insurance plan will be lower depending on how much subsidy you qualify for.In 2017, the federal poverty guidelines were as follows:
| Number of people in family | Federal poverty level |
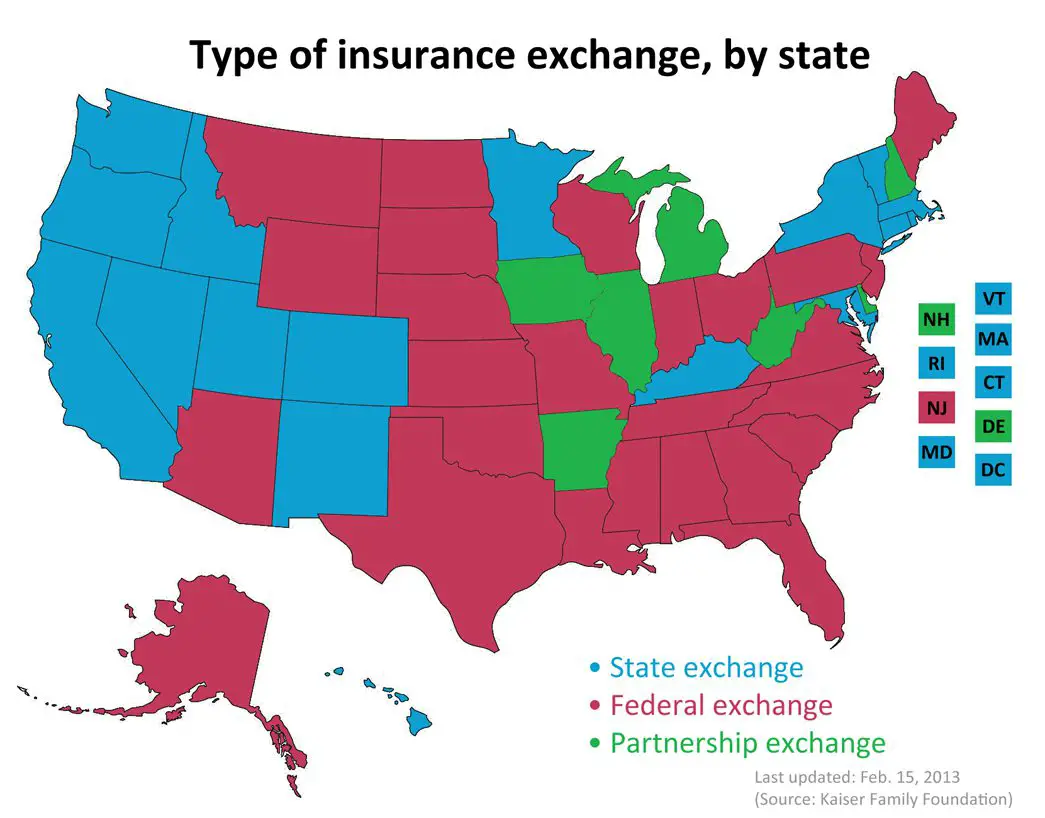
Health Insurance Exchange States By Type1
Heath insurance exchange states fall into one of four categories: aState-Based Marketplace, Federally-Supported State-Based Marketplace, State-Partnership Marketplace, or Federally-Facilitated Marketplace.
State-Based Marketplace: States establish and run their own marketplace. Consumers enroll in coverage through a state-maintained website. States include: CA, CO, CT, DC, ID, MD, MA, MN, NV, NJ, NY, PA, RI, VT, and WA.
Federally-Supported State-Based Marketplace: States establish and run their own marketplace. However, consumers enroll in coverage through the Federal heathcare.gov website.States include: AR, KY, ME, NM, OR, and VA.
State-Partnership Marketplace: These states share responsibility with the federal government. They administer some in-person consumer assistance, while remaining functions are performed by the US Department of Health and Human Services. Consumers use healthcare.gov to enroll. States include: DE, IL, IA, KS, MI, MT, NE, NH, OH, SD, UT, and WV.
Federally-Facilitated Marketplace: US Department of Health and Human Services performs all marketplace functions and consumers enroll through heathcare.gov. States include: AL, AK, AZ, FL, GA, HI, IN, LA, MS, MO, NC, ND, OK, SC, TN, TX, WI, and WY.
46907-HM-0121
Don’t Miss: Starbucks Health Insurance
What Is An Exchange
An Exchange is a mechanism for organizing the health insurance marketplace to help consumers and small businesses shop for coverage in a way that permits easy comparison of available plan options based on price, benefits and services, and quality. By pooling people together, reducing transaction costs, and increasing transparency, Exchanges create more efficient and competitive markets for individuals and small employers.
Historically, the individual and small group health insurance markets have suffered from adverse selection and high administrative costs, resulting in low value for consumers. Exchanges will allow individuals and small businesses to benefit from the pooling of risk, market leverage, and economies of scale that large businesses currently enjoy.
Beginning with an open enrollment period in 2013, Exchanges will help individuals and small employers shop for, select, and enroll in high-quality, affordable private health plans that fit their needs at competitive prices. Exchanges will assist eligible individuals to receive premium tax credits or coverage through other Federal or State health care programs. By providing one-stop shopping, Exchanges will make purchasing health insurance easier and more understandable.
The Difference Between On
“Off-exchange” health insurance refers to health insurance that is not purchased through your state’s health insurance exchange. Each state has an official exchange, established under the Affordable Care Act. Most of them are run by the federal government and use the HealthCare.gov enrollment platform. However, 14 states plus the District of Columbia run their own health insurance exchanges and have enrollment websites that aren’t Healthcare.gov.
If you buy your health insurance through the health insurance exchange in your state , it is considered an “on-exchange” plan. If you buy it directly from the insurance company , it’s off-exchange. Although as described below, some web brokers are able to enroll clients in on-exchange plans using their own websites, via the government’s direct enrollment process.
You May Like: Do Part Time Starbucks Employees Get Benefits
Postponement Of Tax Penalty
On October 23, 2013, The Washington Post reported that Americans with no health insurance would have an additional six weeks before they would be penalized. That deadline was extended to March 31, and those who do not enroll by then may still avoid incurring penalties and getting locked out of the healthcare enrollment system this year. Exemptions and extensions apply to:
- Those living in states that use federal exchange, who may avail themselves of a “special entrollment period” that allows individuals to avoid penalties and enroll in a health plan by checking a blue box by mid-April 2014, stating they tried to enroll before the deadline . The New York Post reports: “This method will rely on an honor system the government will not try to determine whether the person is telling the truth”. State-run exchanges have their own rules several will be granting similar extensions.
- Members of the Pre-Existing Condition Insurance Program, who were given a one-month extension until the end of April 2014.
- Those who have successfully applied for exemption status based on criteria published by HealthCare.gov, who are not required to pay a tax penalty if they don’t enroll in a health insurance plan.
Health Insurance Exchange Example
To visit the health insurance exchange, users go to Healthcare.gov or the website for their state-operated exchange during the enrollment period. Users specify their state and ZIP code, then begin the application.
The documents and information needed to apply are Social Security numbers, income information for the entire family, policy numbers for current insurance and any other information about job-related health insurance.
After completing the application, you can browse the available plans and select the one that matches your needs and your budget. Rather than getting estimates from each company individually, the exchange lists and compares them all in one place. Once you enroll in a plan, you make payments directly to the insurance company rather than to the health insurance exchange.
Not sure if you need to browse the health insurance exchange? Learn more about Obamacare exchanges vs. employer health insurance.
Also Check: Does Starbucks Provide Health Insurance For Part Time Employees
Shopping With Nevada Insurance Enrollment
If youll be shopping for health insurance for 2022, talking to a health insurance agent at Nevada Insurance Enrollment can help you be confident that youre weighing all of your health insurance options and signing up for a plan that fits your needs and budget. Reach out to us today to learn what the next step is in making sure that youre covered in 2020.
Related Articles:
How States Approached The Health Insurance Marketplace Decision
Early adopters A handful of states jumped into exchange planning shortly after the ACA passed. California was the first state to pass legislation authorizing an exchange doing so in September 2010. Colorado, Connecticut, Hawaii, , Oregon, Vermont, and Washington all authorized state-run exchanges in 2011. Massachusetts and Utah were operating exchanges prior to ACA, and both began moving ahead on changes needed to comply with ACA requirements .
In general, it was blue states that moved quickly to establish state-run exchanges in time for the first open enrollment period that began in October 2013, and many of the early adopters had Democratic governors.
Pragmatists A number of states took a pragmatic approach. Despite the uncertainty about the ACA in general and exchange requirements in particular, the pragmatists did enough work to keep their options open.
In some cases, legislatures failed to authorize exchanges, yet federal grants were accepted and spent as executive branches authorized significant planning work to proceed. Minnesota is a good example. While the Republican-controlled legislature failed to authorize an exchange in 2011 or 2012, Democratic Gov. Mark Daytons administration made quiet, extensive progress on an exchange.
Recommended Reading: Does Starbucks Provide Health Insurance For Part Time Employees
Assuring Compliance With Federal Insurance Standards
One challenge has to do with assuring that all QHPs comply with both state insurance laws and the new federal market reforms. Just as the ACA gives states the option to operate their own Exchanges, the ACA continues prior federal policies in which oversight of the insurance market more generally is concerned and gives states the option of taking the lead in enforcing the federal reforms. In states that either refuse to enforce these reforms or else fail to do so, the HHS Secretary steps in following an elaborate process of negotiation with the state. In other words, the law allows HHS to directly enforce federal standards if states, after extensive negotiations, fail to do so. Thus, in FFE states with no established Partnerships, the state also may be one that either declines to or else fails to enforce broader market reforms, leaving HHS in a position of running the entire health insurance market in the state, not just the Exchange. As of February 2013, only Connecticut had enacted comprehensive legislation fully incorporating the federal insurance reforms into its state laws and authorizing their enforcement, and only 10 other states and DC had shown some movement on one or more reforms.
